Last Updated on January 29, 2024 by Pittalks
When it comes to vehicle headlight systems, projector and reflector designs are the two primary types that drivers encounter. Each style has a distinct mechanism for how it illuminates the road ahead, and understanding the differences is critical for any driver considering an upgrade or modification. Projector headlights, recognized for their intense and focused beam, are often found on newer vehicles and are easily spotted by their dome-shaped lenses. On the other hand, reflector headlights have a longer history in the automotive world, with a design that disperses light through a reflective casing behind the bulb.
Determining the best option between projector and reflector headlights hinges on an array of factors, including the type of bulb used, desired brightness, and driving conditions. Upgrading the bulbs—to HID or LED, for example—can significantly enhance visibility, but compatibility with the headlight housing is essential. This comparison aims to illuminate the advantages and limitations of each headlight style, providing drivers with the necessary information to make an informed decision tailored to their needs and preferences.
Reflector Vs. Projector: What makes them different?
There are two primary differences between a projector vs. reflector headlight: the lens design, and the kinds of bulbs that can be used with them. Let’s break each of these down so you can see how that impacts their use and brightness.
Projector vs. Reflector Headlights Comparison Chart
| Reflector | Projector | |
| Generation | Old technology (first developed in 1898) | New technology (first wide-spread use in 1986) |
| Source of Light | Bulb mounted in reflector cup | Bulb light focused by fishbowl lens |
| Main parts | * Reflector bowl * Bulb | * Reflector bowl * Bulb * Lens |
| Typical Size | Small and shallow | Deeper, takes up more space |
| Lighting angle | Wide, but with dark spots | Narrower with no dark spots |
| Best Bulb Types | LED | HID |
How Do Lens Make Projector Headlights Different from Reflector?
Projector headlights incorporate a condenser lens that precisely focuses light, creating a sharp, narrow beam of light. This specific design minimizes scatter and aims to deliver a strong directional output.
On the other hand, reflector headlights use the shape of the reflective bowl to disperse light. They provide a broader beam pattern, but with less intensity and focus, leading to potential dark spots and light waste compared to projector headlights.
Do I Have Projector or Reflector Headlights?
Determining the type of headlights installed in a vehicle can typically be done through visual inspection. Projector headlights are distinct with their visible lens positioned in front of the bulb, which appears similar to a fishbowl. In contrast, reflector headlights will expose the reflective bowl surrounding the bulb, lacking an intermediary lens.
For confirmation, referencing the vehicle’s manual can provide definitive clarity on the headlight type.
LED vs HID: Which Is the Best for Projector/Reflector Headlights?
When it comes to choosing light technology for different headlight designs, LED and HID have their respective advantages:
- LED for Reflector Headlights: LEDs tend to perform better within reflector headlights due to their brightness and ease of installation. However, direct LED replacements for halogen bulbs might necessitate upgrading the reflector to prevent glare to other drivers.
- HID for Projector Headlights: HID, or High-Intensity Discharge lamps, are suited for projector headlights. Offering a higher light output than halogens, they improve visibility when driving at night.
- LEDs in Projector Headlights: While possible, LEDs in projector setups may offer insufficient light compared to HID options, underperforming even against traditional halogen bulbs.
- HIDs in Reflector Headlights: HIDs are generally not recommended for reflector housings due to their intense light output, which can cause excessive scatter, risking the safety of other road users. Additionally, HIDs require a warm-up period and a high-voltage pulse to initiate, posing compatibility issues with standard reflector systems.
To further understand the practical distinction between these headlight types and their compatibility with different light sources, a visual demonstration can be insightful. View a detailed explanation and comparison here.
Projector vs. Reflector Headlights: Detailed Clarification

Reflector headlight technology was the first to be developed. The very first electric headlights installed on a vehicle, all the way back in 1898, used a reflector design. Reflector headlights remain the standard, and are what you’ll find on most cars and trucks when they’re shipped from the factory.
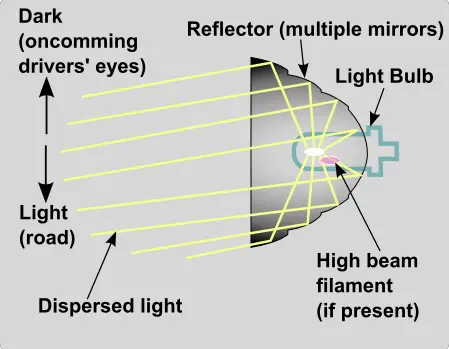
Today’s reflector headlights aren’t drastically different than the ones that have been in use for decades. The main change happened in the 1980s, with the addition of mirrors to the bulb housing. Before that, headlights had to be sealed, forcing drivers to replace the whole housing if the bulb failed. In today’s reflector headlights, it’s easy to access and swap out the bulb or the reflector bowl as needed.
Projector headlights are a more recent invention, and have become increasingly popular in recent years on high-end luxury cars and trucks. They were first used on mass-produced cars in 1986, when they appeared on the BMW 7 Series vehicles.
Early projector headlights used the same halogen bulbs as reflector designs. The 1991 BMW 7 Series was the first to use xenon (HID) lights to expand the brightness potential of the projector headlight. It was after this development the use of projector headlights became more widespread.
Design differences
- Reflector Headlights: Incorporate a simple design where the headlight bulb sits within a bowl or reflector cup lined with a mirrored finish. This creates an even spread of light across the road surface, due to the light reflecting off the bowl:
- Bulb: Situated at the focal point of the reflector for consistent light distribution.
- Bowl: Designed to spread light over a wide area.
- Cost and Size: Generally smaller and less costly due to the simplicity of the design.
- Projector Headlights: Feature a more complex and efficient design using additional components for focused illumination:
- Bulb: Also sits within a reflective bowl but includes a condenser lens to focus the light.
- Lens: A convex lens that projects a focused beam of light onto the road.
- Cutoff Shield: A mechanism for creating a distinct cutoff for low beams, preventing glare to oncoming traffic.
- Solenoid: Engages during high beam operation to move the cutoff shield, allowing a full beam spread.
- Aesthetics: Often sleeker, representing a modern headlight housing design.
How do reflector and projector headlights work?
- Reflector Headlights: Utilize a reflector lens that bounces light off a curved surface within the housing, casting a wide and even light on the road. This design is particularly useful in environments that require a broad illumination:
- Light Output: Can be relatively even but may lack the precise control found in projector systems.
- Beam Pattern: Often lacks a distinct cutoff, which can result in light waste and potential glare for oncoming traffic.
- Projector Headlights: These function by directing a more even distribution of light through a lens. Their key features often include:
- Condenser Lens: Provides a focused and sharp beam pattern on the road surface.
- Focused Light: Creates clear visibility with a distinct cutoff for low beams.
- Low Beam Cutoff: Offers a precise barrier that minimizes glare to oncoming traffic, enhancing safety.
- LED Lights Compatibility: They are often used with various lighting technologies, including halogen, HID, and LED lights.
Pros and Cons
Reflector
Pros
- Wider light angle
- More affordable to make
- Simpler design is easier to repair and maintain
Cons
- Not as bright
- May be prone to dark spots
- Prone to light waste
Projector
Pros
- Brighter, more focused light
- Consistent light with no dark spots
- Less light waste
- Sleek, modern look
Cons
- Cost more
- Narrower light angle
Projector vs. Reflector: Which Is The Best For My Car?
Choosing the best headlight design for your vehicle involves considering brightness, efficiency, and cost.
- Projector Headlights: Offer brighter and more uniform illumination. They are more efficient by focusing light precisely on the road.
- Reflector Headlights: Standard in many vehicles; however, they scatter some light, leading to less efficient usage.
Installation Costs:
- Converting from reflector to projector headlights can cost between $200-$300.
- Upgrading current halogen bulbs to LED via a conversion kit is cost-effective at $20-$40.
Upgrade Choice:
- Vehicles with existing projector setups may only need new bulbs.
- For reflector headlights, evaluate the benefits of installing projector units against the investment required.
The Final Words
- Upgrading to LED bulbs in reflector headlights is a cost-effective method to enhance brightness.
- Modifications may be required when switching to LED, yet it remains economically favorable compared to alternative upgrades.
- Opting for projector headlights with an HID bulb maximizes visibility during night driving.
- Projector setups offer superior illumination and design, ensuring safety on even the most unlit roads.
Frequently Asked Questions
Light Distribution: Projector headlights provide a more focused and directed beam of light, reducing scatter and improving visibility.
Brightness: Reflector headlights can appear brighter within their dispersed area, but the concentration of light in projectors can enhance visibility in the direction they are aimed.
Beam Pattern: The beam pattern of projector headlights is sharper with a more distinct cutoff than reflectors, preventing glare to oncoming traffic.
Conversion Kits: Conversion kits are available, allowing for the switch from reflector to projector headlights.
Installation: The process involves removing the old headlight assembly, installing the new projector housing, and ensuring proper alignment for optimal performance.
Professional Help: It’s recommended to seek professional installation to ensure proper fitting and beam alignment.
Advantages:
Energy Efficiency: LED bulbs consume less power, extending battery life.
Longevity: LEDs typically last longer than halogen or HID bulbs, meaning less frequent replacements.
Disadvantages:
Heat Dissipation: LEDs can generate significant heat, which can be challenging to manage in the confined space of a projector housing.
Cost: Upfront costs for LED bulbs are higher compared to traditional halogen bulbs.
Visibility: Projector headlights offer better visibility at night due to their focused beam of light.
Glare Reduction: They reduce glare to oncoming drivers, which is beneficial during night driving.

