Last Updated on June 26, 2023 by Pittalks
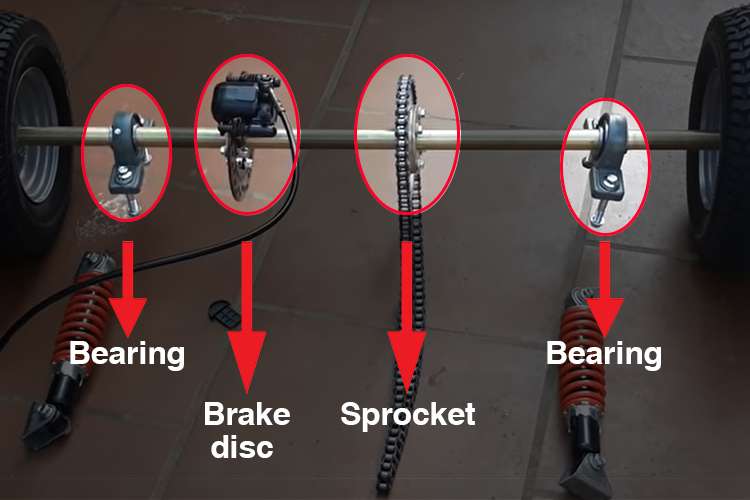
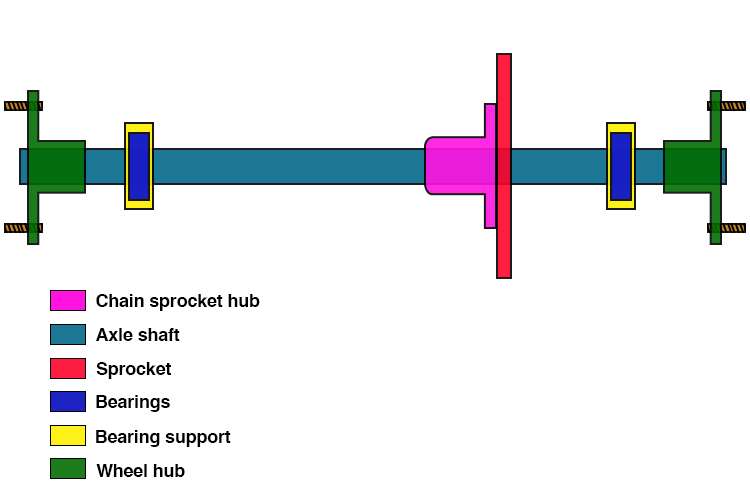
A live axle is responsible for carrying the load and transferring the power from the engine to the wheels. It also includes a brake disc and bearing couple for attaching the axle to the chassis.
Basic functions:
- Support the weight of the back of the kart
- Transmit engine torque
- Transmit braking torque
How does a live go-kart work?
The engine directly transfers power to the sprocket (in a go-kart, usually people use a drive chain), which turns the axle and then turns the wheels. This makes both rear wheels spin at the same speed.
The 2 bearings keep the axle spinning without friction. And of course, the brake disc is used to stop the kart using hydraulic calipers.
Those who are interested in drift must have heard of the concept of locked differential. In fact, live axle and locked differentials work somewhat the same way.
The rotation of both wheels at the same speed in the corner makes it possible to drift. However, in the go-kart, we want to turn the corners quickly and sharply, not slowly and slippingly. Although this is a disadvantage for the live axle, the power efficiency and other advantages make the live axle more attractive to go-karters.
Pros
- Efficient power transfer
- Easy to install and maintain
- Less likely to fail
- Cheaper
Cons
- Skidding on turns
Go-kart live axle vs. differential
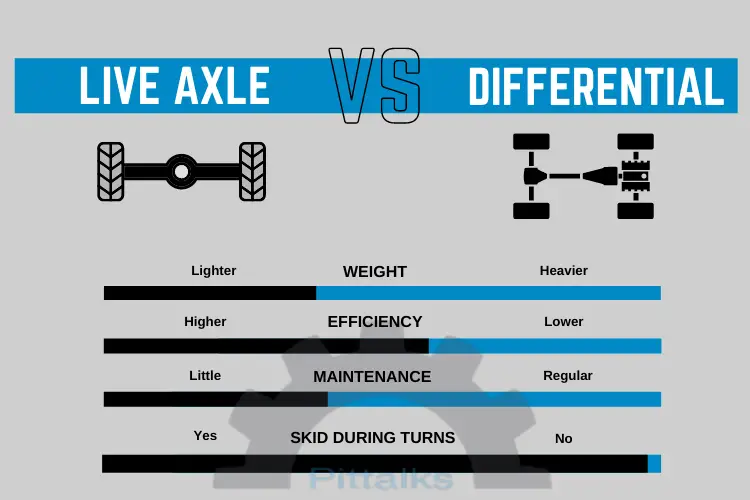
Differential transfer the movement coming from the shaft independently to both wheels. This means differentials allow the wheels to spin at different speeds at once.
Although they are good for handling, they cause power loss in transmission. It is also relatively difficult to use on a go-kart.
A live axle is much more straightforward. It’s similar to the transmission system on bicycles. You can think of the pedal as the engine. The chain is responsible for the same job for bicycles and go-karts. That is to directly transfer the power to the wheel(s). If your bike had two rear wheels, it would definitely be a live axle.
In case of a differential, the engine torque is transfered via a shaft. This shaft rotates between the engine and the differential. The differential distributes this rotational movement to the right and left wheels independently.
This gives you an easy turn because the inner wheel can spin slower than the outer wheel. However, differentials need both wheel touch ground to work (live-axle doesn’t need it).
This leads to another concept of go-kart racing. To achieve optimal cornering, your go-kart can’t just keep 4 wheels on the ground all the time. That would be too skitting and slow. So, when your go-kart corners, you want to get the inner rear wheel off the ground.
Actually, the “lifting” is usually not visual. Sometimes, it’s just a reduction of load on the inner wheels and an increase of load on the outer wheels.
The effect of live axles stiffness on performance
The flexibility of a live axle offers us different racing experiences. These, in turn, affect braking performance and handling on corners. What are those types?
- Soft
- Medium
- Hard
Many factors determine a live axle’s stiffness:
- Axle length – the longer, the more flexible
- Diameter and wall thickness – the higher, the less flexible
- Different heat treatment
- Surprisingly, the material itself has an insignificant effect on the live axle’s stiffness.
To understand why stiffness is so important in go-kart racing, you need to know the “rate of lift.”
In the part above, I explained why “lifting” is used in go-kart racing. Now, “rate of lift” is the technical term for how quickly the kart rises when it lifts.
Under the conditions where the track is very slippery, or it’s a small sprint track, you want a high rate of lift so that the karts can lift quicker and have a sharper turn (inner rear wheel has more grip.)
On the other hand, if the track has wide corners or is grippy enough, a low rate of lift is the way to go, and you won’t have oversteering problems (inner rear wheel has less grip.)
Back to the problem, why does your live axle’s stiffness has anything to do with these?
Take a look at the images below.
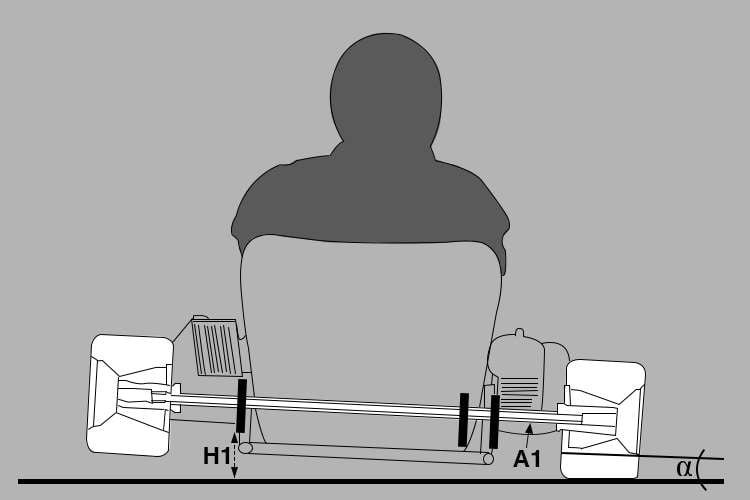
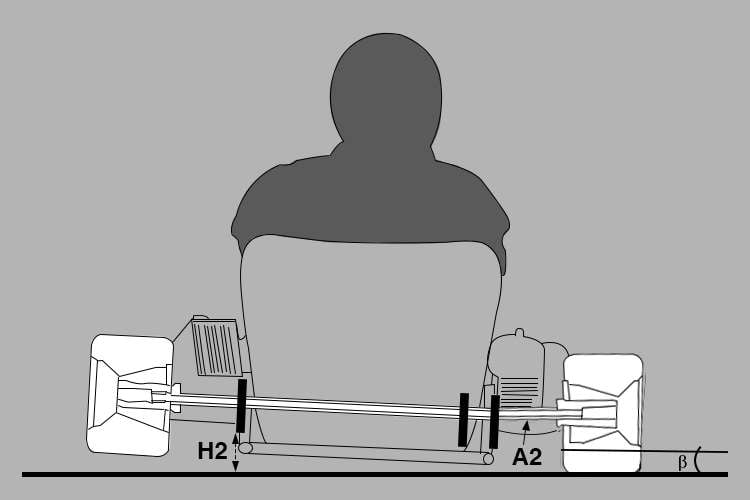
- H1>H2
- A2 flexes more than A1 does
- Alpha > Beta
When your axle is softer (below image), the part from the outer bearing to the outer wheel (A) flexes more. This results in H2 lower than H1 (height from the ground to the inner bearing), and the Beta angle is also smaller than alpha. Therefore, the harder live axle (above image) causes the center of gravity lean to the outer side, putting more load on the outer wheels.
Eventually, a harder axle will offer a better grip when corning, and it’s suitable for sprint races. On the other hand, a softer axle is suitable for tracks having wide corners.
Short vs. long axle
The length of your axle directly affects the handling.
While shorter axles provide sharper turning, they are more prone to skidding during braking.
Long axles, on the other hand, are safer. Of course, this causes them to lose their agility during the turn. You should swap to a longer axle in case your kart oversteers.
That’s why you should pay attention to the length of the axle. As you can see, everything works together and they all have important effects on each other.
Dead axle vs. live axle
Unlike the dead axles and most differential systems in cars, the working principle of go-kart axles is fundamentally different. The dead axle is idle. They have nothing to do with power transmission, they just act as carriers.
Go-kart rear axle setup
Go-kart rear axle setup is quite straightforward, you can watch the video below and learn how to do it yourself.
Some tips to choose the suitable live axles for your go-kart
Know what you need.
Generally, if you’re understeer in corners, it means you need a harder and shorter axle.
But if you like a drifting go-kart (it feels really good to drive one, just slow), or your kart oversteers, you need softer axles.
Also, aluminum and carbon fiber are lighter than steel. Choosing them will have a good effect on your hp/weight ratio. But your budget is also an important factor here.
Go-kart rear axle diagram
Related articles

Where can I drive my go-kart legally?
If you want to drive your go-kart, you can do it in approved designated locations. Places include private property, karting tracks, designated dirt trails, …

How fast do go-karts go? [Speed chart]
The answer depends on a couple of things, including engine classes and whether or not the engine is a 2-stroke or a 4-stroke. Typically, a 4-stroke 125cc go-kart …